What is kidney disease?
The kidneys filter the waste products and water into your bloodstream like urine. Chronic kidney disease causes your kidneys to lose their function over time. The last stage of kidney disease is the last stage of chronic kidney disease. It means your kidneys are no longer functioning well enough to meet the needs of daily life.
End-stage kidney disease is also called end-stage renal disease (ESRD). The kidneys of people with ESRD are less than 10 percent of their normal capacity, which may mean that they are not working or not at all.
Kidney disease usually progresses. The length of each stage varies depending on how your kidney disease is treated, especially concerning your diet and whether your doctor recommends dialysis. Chronic kidney disease usually does not reach the final stage until 10 to 20 years after your diagnosis. ESRD is the fifth stage of chronic kidney disease progression, measured by your glomerular filter (GFR) scale:
- GFR Stage (ml / min / 1.73 m2) Kidney health.
- 1 ≥90 kidney function normally, but early signs of kidney disease appear.
- 2 60-89 kidney function decreased slightly.
- 3A / 3B 45-59 (3A) and 30-44 (3B) kidney function decreases significantly.
- 4 15-29 kidney function decreased significantly.
- 5 <15 ESRD, also known as guaranteed kidney failure.
What causes chronic kidney disease?
Many kidney diseases affect the nephrons, small kidney filters. This leads to improper blood filtering, which eventually leads to ESRD. ESRD is mainly caused by diabetes and high blood pressure.
If you have diabetes, your body cannot break down glucose (sugar) properly, so your glucose levels remain high. Having high blood glucose levels damages your nerves.
If you have high blood pressure, an increase in pressure in your small arteries leads to injury. Damage prevents your blood vessels from carrying out their filter functions.
Other causes of ESRD include:
- Prolonged obstruction of the urinary tract by kidney stones, enlarged prostate, or certain types of cancer.
- Glomerulonephritis is an inflammation of the kidney filters (known as glomeruli).
- Vesicoureteral reflux, in which urine flows into your kidneys
- At abnormal birth.
Who is at risk for end-stage kidney disease?
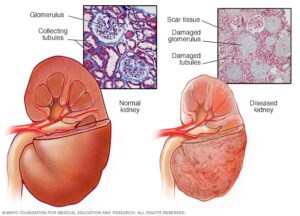
Some people are at high risk of developing ESRD, such as people who:
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Relatives with ESRD
Your risk of developing ESRD also increases if you have any type of kidney condition, including:
- Polycystic kidney disease (PKD)
- Alport syndrome
- interstitial nephritis
- Pyelonephritis
- Certain autoimmune conditions, such as lupus.
According to some studies, a rapid decrease in kidney function may indicate the onset of ESRD.
What are the symptoms of late kidney disease?
You may have a variety of symptoms, including:
- Decreased urination
- Inability to urinate
- Fatigue
- Malaise, or a general feeling of illness
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of food
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dry skin and itching
- Changes in skin color
- Bone pain
- Confusion and difficulty concentrating
Other symptoms may include:
- Easy damage
- Frequent bleeding from the nose
- Numbness in your hands and feet
- Evil spirit
- Excessive thirst
- Constant confusion
- Lack of menstrual cycles
- Sleep disorders, such as obstructive sleep apnea and restless leg syndrome (RLS)
- Low libido or impotence
- Edema, or swelling, especially in your legs and hands
See your doctor immediately if any of these symptoms affect your health, especially if you are unable to urinate or sleep, vomit frequently, or feel weak and unable to perform daily activities.
How is kidney disease diagnosed?
Your doctor examines the ESRD using physical examination and testing to check your kidney function. Kidney function tests include:
- Urine analysis: This test helps your doctor check the protein and blood in your urine. These things indicate that your kidneys are not working properly.
- Serum creatinine testing: This test helps your doctor check whether creatinine is growing in your blood. Creatinine is a toxin that your kidneys need to filter out.
- Blood urea nitrogen test: This test helps your doctor check how much nitrogen is in your blood.
- Glomerular filtration rate (GFR): This test allows your doctor to estimate how well your kidneys are filtering waste.
How is late kidney disease treated?
ESRD treatment dialysis or kidney transplantation. In some cases, a change in lifestyle and medication may be helpful.
Dialysis
You have two options when doing dialysis.
Another method is hemodialysis, which uses a machine to process your blood. The machine filters garbage using a solution. Then it returns pure blood to your body. This method is usually used three times a week and takes three to four hours each time.
Your doctor may also give you peritoneal dialysis. This procedure involves placing a solution in your stomach that is then released using a catheter. This type of dialysis can be done at home with proper training. It is usually done at night while you sleep.
Kidney transplantation
Kidney transplant surgery involves removing your affected kidneys (if removal is required) and replacing a donated organ. Only one healthy kidney is needed, so donors often live. They can donate one kidney and continue to function normally with another. According to the National Kidney Foundation, more than 17,000 kidney transplants were performed in the United States in 2014.
Drugs
People with diabetes or high blood pressure should control their condition to help prevent ESRD. Both cases benefit from drug treatment using angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors) or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs).
Lifestyle changes
Storing fluids can cause rapid weight changes, so monitoring your weight is important. You may also need to increase your caloric intake and reduce your protein intake. Foods low in sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes may be needed, as well as a fluid restriction.
Limit these foods to avoid eating too much sodium or potassium:
- Bananas
- Tomatoes
- Oranges
- Chocolate
- Nuts and peanut butter
- Spinach
- Avocado
Taking supplements, such as calcium, vitamin C, vitamin D, and iron, can help your kidneys function and absorb essential nutrients.
What are the complications of end-stage kidney disease?
Possible ESRD issues include:
- Skin diseases on dry skin and itching
- Increased risk of infection
- Abnormal electrolyte levels
- Pain in joints, bones, and muscles
- Weak bones
- Nerve damage
- Changes in blood glucose level
Kidney transplants may also be effective. The rates of failure of transplanted kidneys are low, ranging from 3 to 21 percent in the first five years. The implant allows you to resume normal kidney function. If you follow your doctor’s recommendations regarding diet and lifestyle changes, kidney transplants can help you live free of charge for ESRD for many years.
What is the long-term vision?
The development allows people with ESRD to live longer than ever before. ESRD can be dangerous to health. With treatment, you will probably live many years later. Without treatment, you can only live without your kidneys for a few months. If you suffer from other health problems, such as heart problems, you may be facing additional problems that could affect your life span.
It can be easy to withdraw as you experience the effects of ESRD or lifestyle changes that come with dialysis. If this happens, seek professional help or support from your family and friends. They can help you to stay active in your daily life. This can ensure that you maintain a high standard of living.
What can prevent chronic kidney disease?
In some cases, ESRD is inevitable. However, you should control your glucose levels and your blood pressure. You should always call a doctor if you have symptoms of ESRD. Early detection and treatment can delay or prevent the disease from progressing.
