There are many types of heart disease and each has its own symptoms and treatment. For some, lifestyle changes and medication can make a huge difference in improving your health. For others, you may need surgery to get your ticker working properly again.
Learn about some common types of heart disease and how to prevent them, as well as how they are treated.
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
CAD is the most common heart problem. With CAD, you can get blockages in your coronary arteries — the vessels that supply blood to your heart. This can lead to reduced blood flow to your heart muscle, preventing it from getting the oxygen it needs. The disease usually begins as a result of atherosclerosis, a condition sometimes called hardening of the arteries.Coronary heart disease can give you chest pain, called angina pectoris, or lead to a heart attack.
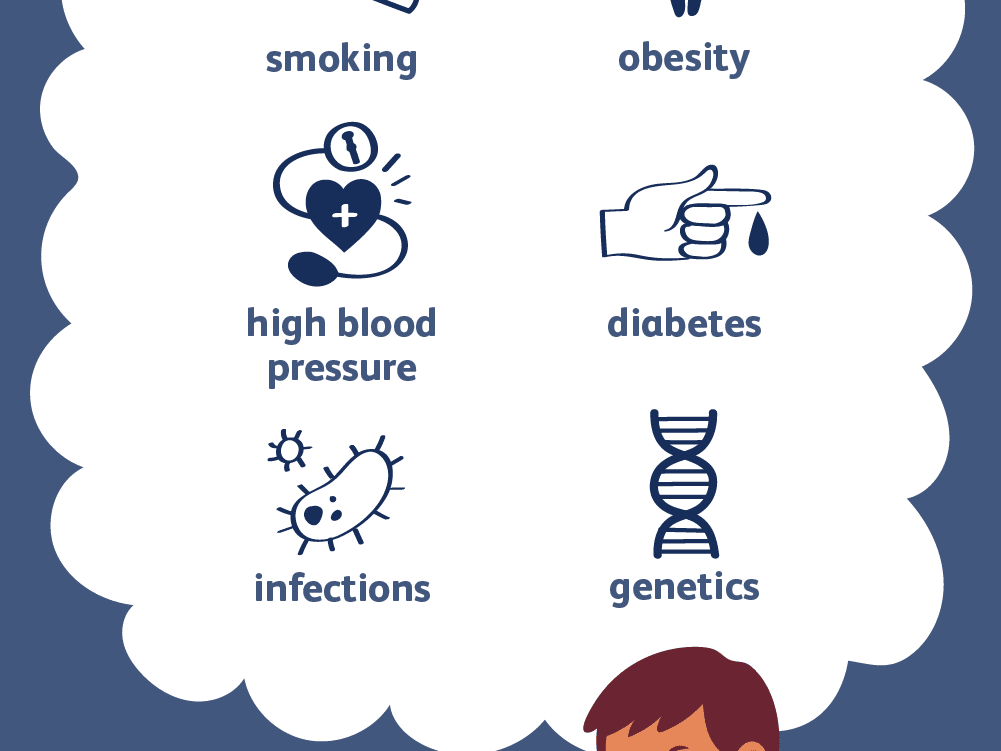
Some things that can put you at higher risk for coronary artery disease are:
- Age (For men, the risk of heart disease increases after age 55; for women, the risk increases sharply after menopause.)
- Be inactive
- You have diabetes or metabolic syndrome
- Family history of ischemic heart disease
- Genetics
- High blood pressure
- A high level of LDL “bad” cholesterol or a low level of HDL “good” cholesterol
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Stress
Cardiac arrhythmia
When you have an arrhythmia, your heart has an irregular rhythm. Serious arrhythmias often develop from other heart problems, but they can also occur on their own.
Heart Failure
In heart failure, your heart doesn’t pump blood as well as it should to meet your body’s needs. It is usually caused by coronary artery disease, but it can also happen because you have thyroid disease, high blood pressure, heart muscle disease (cardiomyopathy), or some other conditions.
Heart valve disease
Your heart has four valves that open and close to control the flow of blood between the heart’s four chambers, lungs, and blood vessels. The abnormality could make it difficult for the valve to open and close properly. When this happens, your blood flow may be blocked or blood may leak. Your valve may not open and close properly.
Causes of heart valve problems include infection such as rheumatic fever, congenital heart disease, high blood pressure, coronary artery disease or as a result of a heart attack.
Diseases of heart valves include
Endocarditis. This is an infection that is usually caused by bacteria that can enter the blood and take root in your heart during illness, surgery, or after using intravenous drugs. This often happens if you already have problems with the valves. Antibiotics can usually cure it, but the disease is life-threatening without treatment.
If your heart valves are severely damaged due to endocarditis, you may need valve replacement surgery.
Rheumatic heart disease. This condition develops when your heart muscle and valves are damaged by rheumatic fever, which is associated with strep and scarlet fever.
Rheumatic heart disease was more common earlier in the 20th century. But doctors can now prevent it by using antibiotics to treat the diseases that lead to it. If you get it, symptoms usually appear many years after infection.
Pericardial disease
Any disease of the pericardium, the sac that surrounds your heart, is called pericardial disease. One of the more common diseases is pericarditis, or inflammation of the pericardium.
It is usually caused by a viral infection, inflammatory diseases such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, or injury to the pericardium. Pericarditis often follows open heart surgery.
Cardiomyopathy (heart muscle disease)
Cardiomyopathy is a disease of your heart muscle, or myocardium. It stretches, thickens or hardens. Your heart may be too weak to pump well.
There are many possible causes of the disease, including genetic heart disease, reactions to certain drugs or toxins (such as alcohol), and infections caused by a virus. Sometimes chemotherapy causes cardiomyopathy. Doctors often cannot find the exact cause.
Congenital heart disease
Congenital heart disease happens when something goes wrong while the heart is forming in a baby while it’s still in the womb. A heart abnormality sometimes leads to problems right after birth, but other times no symptoms appear until you become an adult.
Septal abnormalities are among the most common congenital heart problems. They are the holes in the wall that separate the left and right sides of your heart. You can get the procedure to patch the hole.
Another type of abnormality is called pulmonary stenosis. A narrow valve causes a decrease in blood flow to your lungs. A procedure or surgery can open or replace the valve.
In some babies, a small blood vessel known as the ductus arteriosus does not close properly at birth. When this happens, some of the blood leaks back into the pulmonary artery, putting a strain on your heart. Doctors can treat it with surgery or a procedure, or sometimes with medication.
