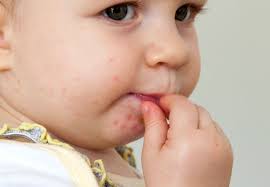
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Trusted Source, HFMD is generally not serious in adults or children.
The CDC notes that most people from a trusted source recover from HFMD in 7-10 days without medical treatment. However, children under 2 years of age may remain sick longer.
The American Academy of Dermatology Association (AADA) states that most adults do not have symptoms if they contract HFMD. Those who do will generally have benign symptoms.
Complications requiring medical intervention occur very rarely.
Symptoms in adults
The symptoms of HFMD in adults are the same as in children.
Symptoms may include:
- mouth ulcers
- an itchy rash on the hands, feet, or both
- fever
- flu-like symptoms
How long does HFMD last in adults?
According to the AADA, most signs and symptoms of HFMD go away within 7-10 days.
However, the CDC notes that people can spread the virus days or weeks after symptoms disappear and if they had no symptoms at all.
Causes
- Enteroviruses cause HFMD. According to the CDC, the viruses that most commonly cause illness by Trusted sources include:
- Coxsackievirus A16: This virus is the most common cause of HFMD in the United States.
- Coxsackievirus A6: People who become infected with this virus may experience more severe symptoms.
- Enterovirus 71 (EV-A71): This virus is the most common cause of HFMD in East and Southeast Asia.
Diagnosis
A doctor diagnoses HFMD by performing a physical exam. This exam may include the doctor:
- examining rashes around a person’s mouth, feet, and hands
- asking the person about their symptoms
- taking a throat swab or stool sample to check for the virus
- The doctor may also consider the person’s age. Children aged 5 and younger are most likely to get the disease. The person should inform the doctor if they have been in contact with a child with the virus.
Therapy
According to the CDC, almost all cases of HFMD resolve within 7-10 days without medical intervention.
However, a person can treat HFMD symptoms at home by:
- taking over-the-counter pain relievers (acetaminophen or ibuprofen) to help reduce pain and fever
- drink plenty of water and other fluids to prevent dehydration
- using a numbing mouthwash to relieve the pain of mouth ulcers
- avoiding hot, spicy, or acidic foods
An adult may not need any treatment if they have no symptoms of infection.
Recovery
If a person has symptoms, they should clear up with or without treatment within 7-10 days. Adults may want to take a few days off work if they have severe symptoms.
It’s important to remember that the virus can be passed on to others days or weeks after symptoms subside.
Preventative steps, including frequent hand washing and avoiding close contact with others, can help stop the spread of HFMD.
Even people without symptoms can transmit the virus. However, asymptomatic adults usually do not realize they have the infection, so they are likely to continue with their lives as usual.
Complication
In most cases, the risk of complications from HFMD is low.
The biggest risk is dehydration. The CDC also identifies the following rare complications:
- loss of fingernails or toenails
- encephalitis or polio-like paralysis
- viral or aseptic meningitis
People who are pregnant should notify a health care professional if they develop symptoms of HFMD or have been in contact with someone with the virus.
Prevention
One can take steps to avoid the disease. Many of the methods for preventing HFMD are also good for preventing other illnesses, such as the common cold. Measures to reduce the risk of infection include:
washing hands often and thoroughly
avoiding close contact with people who have HFMD
regularly wash and disinfect surfaces and objects that are in contact
Can adults work with HFMD?
Although most adults with HFMD do not experience symptoms, they can still be contagious and can spread the virus to others.
People can remain contagious for days or weeks after their symptoms subside.
Therefore, people with HFMD should not go to work and should isolate themselves at home to prevent the disease from spreading.
When to consult a doctor
An adult with HFMD may not need to talk to a doctor. However, if they experience fever, mouth ulcers, or ulcers on their hands or feet, they may want to seek medical attention.
Parents or caregivers of young children who develop HFMD symptoms may not need to see a doctor if they can manage the symptoms at home.
However, children or adults should see a doctor if their symptoms do not improve within 10 days or are severe.
People with weakened immune systems should talk to a doctor about HFMD, especially if their symptoms are severe. People who get HFMD during pregnancy should also notify a health care provider.
A parent or carer should talk to a pediatrician if their child shows signs of infection, especially if other children at their school or nursery have the disease.
They should also seek medical attention if the child has severe symptoms, is very young, or is unable to eat or drink enough fluids.
View
Although adults can get HFMD, they often have no symptoms, so they may not realize they have contracted the virus.
Those with symptoms can expect a full recovery within 7-10 days.
Summary
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a common viral infection. Infants and young children are most susceptible, but it can sometimes affect adults and older children.
People can reduce their risk of contracting the virus by avoiding sick people, washing their hands regularly, and not sharing drinks or food with others.
Treatment usually involves managing symptoms if any occur. A person can expect to recover in about 7-10 days.
