All modern hospital beds are flexible, and patients can adapt to their changing needs. What distinguishes different types of hospital beds is what empowers their functions.
All modern hospital beds are flexible, and patients can adapt to their changing needs. What distinguishes different types of hospital beds is what empowers their functions.
The WHO describes a hospital bed as a bed that is regularly maintained and staffed accommodation and full care of consecutive inpatients and is available wards or part of a hospital where there is ongoing health care for inpatients provided. The total number of such beds includes a common bed at the hospital.
Statistics on available hospital beds do not include newborn beds, day care beds,temporary and temporary beds, barns, and beds for special purposes such as dialysis or delivery (WHO, 2000a). OECD Health Data currently avoids the term “hospital beds” and uses the term.
“Patient beds”. These are also classified into “medical care beds” or “acute care beds ”,“ mental care beds ”and“ long-term caregivers ”. EUROSTAT has introduced another small group namely “other beds”. Inpatient care beds accommodate officially admitted patients (or ‘Hospitalized’) at the hospital for treatment and / or care and at least a minimum stay one night in the hospital. Hospital beds are available on the same day or kindergarten patient care is usually not included in the “complete patient care” calculations. Ibala inpatient beds refers to the “available beds” count.
The total number of hospital beds is permanent hospital beds is maintained and staffed and is readily available to care for recipients patients.
Entries:
Beds in all hospitals, including general hospitals (HP.1.1 in the program
Classification of Health Accounts (SHA) providers, mental health and
drug abuse hospitals and other specialized hospitals
Cramped and unoccupied beds.
Excluded:
Surgical tables, rescue vehicles, emergency wrists, day care beds, and healthy baby beds.
Beds in wards were closed for any reason.
Temporary and temporary beds.
Beds in Nursing and Residence Centers (HP.2).
Acute care beds in hospitals (HP.1) are hospital beds are available for medical care (HC.1 in the SHA category externally
psychiatry).
Entries:
Patient beds where the main clinical objective will be performed one or more of the following: birth control (childbirth), non-psychiatric treatment illness or to provide direct treatment for injuries, to perform surgery, to relieve symptoms of non-psychiatric illness or injury (without palliative care), to reduce the severity of non-mental illness or injury, prevent exacerbation and / or problem of non-mental illness and / or injury which may threaten life or normal activities, perform diagnoses or therapeutic procedures.
Excluded:
Beds assigned to other care services (such as mental health care, rehabilitation, long-term care and palliative care).
Hospital beds for mental health and drug rehabilitation (HP.1.2).
Rehabilitation beds (HC.2 in SHA care categories).
Palliative care beds.
Hospital psychiatric beds (HP.1) are permanent hospital beds
patients with mental health problems (section HC.1 in the SHA category).
Entries:
All beds in mental health and drug hospitals (HP.1.2).
Beds in the general psychiatric departments of hospitals (HP.1.1) and
specialized hospitals (excluding mental health and substance abuse).
Excluded:
Beds assigned to non-psychiatric care (section HC.1).
Beds allocated for long-term care by hospital nurses (HC.3).
Rehabilitation beds (HC.2).
Palliative care beds.
Long-term hospital beds (HP.1) are permanent hospital beds
patients in need of long-term care due to chronic disability and a
a reduced level of independence in the activities of daily living.
Entries:
Beds in long-term care departments of general hospitals (HP.1.1).
Specialized long-term care beds (excluding mental health as well
drug abuse hospitals) (HP.1.3).
Palliative care beds
Handmade beds

A bed that does not have the power to repair electrical equipment is called a Hand Hospital Hospital Bed. These types of beds often have hand-splitting that can be used to adjust the shape of the beds. The hand crank is usually found near the foot or head of the bed.
Electric Beds

These types of beds often offer a combination of manual and electrical adjustments. Usually, the height of the beds can be adjusted by hand with the help of a hand crank. However, head and foot adjustments can be made by touching the buttons placed next to the user’s hand. Also, check the types of pillows.
Medical facilities often use automatic hospital beds that can be operated with the click of a button. For these types of beds, head and foot adjustments, and lengths can be used without the manual intervention of the user or caregiver. In addition, the automatic hospital beds also provide some of the positions/changes mentioned below.
Trendelenburg Position: In this position, the entire bed is tilted 15-30 degrees, with the user’s feet above his or her head. This position is used to regulate blood flow.
Trendelenburg Depression Position: This position is directly opposite the Trendelenburg area, with the user’s head above their feet. This position is used to help breathe and reduce stress.
Heart Chair: Patients with heart surgery as respiratory problems are believed to recover faster if they spend more time sitting upright. Many automatic beds are usually designed with a combined char charging shape. With the help of this position, the patient or caregiver can shift the bed from the floor to the heart seat using the buttons located on the bed, with minimal user movement.
Bariatric Beds

Bariatric beds are usually larger and stronger than regular hospital beds. These beds include a larger bed and special mattresses to accommodate bariatric patients. These heavy beds can accommodate 1200 pounds of users and can be up to 54 “x 88”.
Lower beds
The lower beds are the same as the standard hospital beds. They can work by hand with full power. However, the only additional function is that they offer a wide range of length adjustments. They allowed the bed frame to be lowered almost to the floor. These beds are designed to prevent the patient/user from falling out of bed. They are specially designed for patients with mobility problems to get out of bed.
Hospital Nursing

Also known as safety beds, hospital kindergartens are specially used for children who may be at risk of falling out of bed. They usually have high heels on all sides of the beds. It prevents the baby from getting out of bed itself. Basically, they are designed for the safety of children recovering or in need of health care.
Gatch Beds
Gatch beds are often used by medical facilities and areas that may be deficient. These are the most durable and effective medical beds. The Gatch bed usually consists of three adjustable sections, which are activated with the help of the spring method. The three moving parts include the head, knee, and foot. These beds also allow patients to stay upright to help with breathing. The only consequence of this type of bed is that they may need the help of a caregiver to adjust to different positions.
Liquid Air Beds
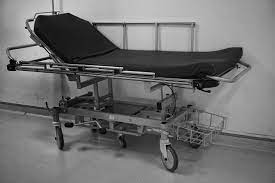
Liquid air beds are especially used by health care facilities for patients with ulcers that are difficult to heal. These types of beds usually distribute the patient’s weight evenly over a full mattress. These beds provide air-controlled ventilation through small holes to reduce pressure on the patient’s body. They are designed to create the ideal environment for wound healing by controlling factors such as friction, temperature, pressure, and humidity. These beds are for specialized hospitals only and cannot be used for long-term recovery or home care.
Freedom Beds

This is one of the most popular types of hospital beds available on the market. It uses a 3-step rotation stage that can help rehabilitate patients as smoothly as possible, without interruption. The seamless bed rest regimen prevents any type of stress injury in patients who stay in bed longer. One of the unique features of Freedom Bed is its air system, located between the platform and the mattress, which allows users to automatically reset even when their upper body is in a raised position. By all means, this is one of the latest and most comfortable medical beds available to anyone.
Collapsible hospital beds
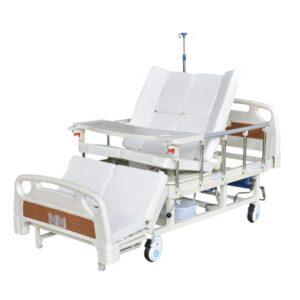
Suitable for patients recovering from fractures other than bedridden patients. These beds are ideal for patients with a variety of reading and sleeping needs.
Powerful ICU beds with a car
If you need beds for patients with a little independent work then these engine-driven ICU beds should be your choice. These beds provide great comfort to patients with severe disabilities. Other than that, these beds are ideal if you have a few staff members.
Critical care beds
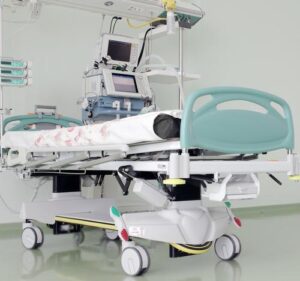
An ICU bed is a bed specially designed for patients under the intensive care unit. ICU beds are usually made of antibacterial or anti fungal agents (with most hospital equipment), but ICU bed manufacturers make them the same way as other beds.
Long-term care beds

Long-term care beds in hospitals are hospital beds that accommodate patients in need of long-term care due to chronic disability and reduced level of independence in daily activities.
Changing Hospital Beds
Adjustable beds have been used in hospitals for a long time, [4] but have been widely used in home care for the past three decades, as they have been found to provide comfort in a variety of conditions. They can help provide comfortable sleep for those recovering from surgery, helping with circulation, breathing and inflammation. Adjustable beds used in hospitals and home care are the same for basic operations.
Special Hospital Beds
Special Hospital beds are special medical beds that meet the needs of specific patients, be it patient size, conditions of care, or medical needs. These beds are designed with specific details in mind, and as a result, each bed serves a very different purpose in the treatment of the patient.